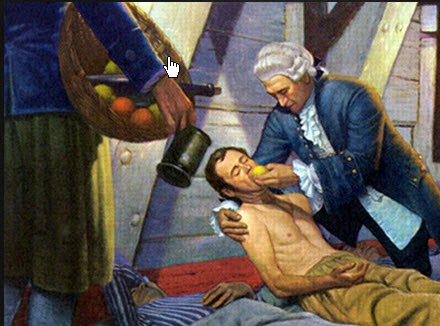
 Most of us know about scurvy and how it killed more sailors than other diseases and battles, and was simply cured by giving sailors lemons or limes.
Most of us know about scurvy and how it killed more sailors than other diseases and battles, and was simply cured by giving sailors lemons or limes.When the vitamin C level in many patients in hospital, particularly those who are seriously ill is measured, it is often near scurvy levels, and because vitamin C is essential for holding the cells together, maintaining the immune system, fighting infections and cancer, and many other functions, one wonders how many patients in intensive
care and hospital beds do not recover simply because of low vitamin C levels. (In hospital they regularly measure electrolytes, kidney and liver function etc – but never vitamin C levels!)
I have had personal experience and seen the benefit of intravenous vitamin C, or even high dose oral vitamin C in patients with infection and cancer, it provides enormous hope for people with cancer, especially advanced disease. I will write about this in a later blog, but I felt the article below written by one of the world authorities on vitamin C (Dr Thomas Levy) is worth sharing with the rest of the world. The more people who know about the value of this essential vitamin and its potential use in many diseases, the more rapidly conventional medicine and doctors will start introducing into their treatment regimes.
Is
the healing power of Vitamin C too good to be true? Can this inexpensive and
convenient vitamin improve and heal the toughest of ailments?
by Thomas E. Levy, MD, JD
My ongoing relationship with vitamin C
now spans a full 20 years, when I first


















